
Dr. Adam Badra Cahaya received his B.Sc, M.Sc and Dr. Sc. in 2013, 2015 and 2018, respectively, from Department of Physics, Tohoku University. He received Dr. Sc. degree with dissertation entitled “Spin, charge and heat coupling at magnetic interfaces” from Interdepartmental Doctoral Degree Program for Multi-Dimensional Material Science Leaders. His doctoral study was done in Institute for Materials Research Theoretical Physics Group under JSPS Research Fellowships for Young Scientist.
Email: adam [at] sci.ui.ac.id
2008 Satyalancana Wira Karya from Presiden Indonesia
2012 Young Scientist Award from Aoba Society for the Promotion of Science 青葉理学振興会奨励賞.
2023 “Modeling of Electrical Control of Exchange Bias for Efficient Magnetic Recording” from Indonesia Toray Science Foundation
2022 – 2023 “Pemodelan Teoretis Produksi Arus Memanfaatkan Spin Nuklir” from Univ. Indonesia
2022 – 2023 “Pemodelan Teoretis Mekanisme Produksi Arus Listrik Memanfaatkan Impuritas Logam Tanah Jarang” from Univ. Indonesia
2022 – 2023 “Pemodelan Teoretis Mekanisme Kontrol Magnetisasi Memanfaatkan Interaksi Spin-Orbit Antarmuka” from Univ. Indonesia
2020 – 2021 “Pemodelan Teoritis Struktur Pita Elektron dari Semikonduktor untuk Aplikasi Konversi Energi” from Univ. Indonesia
2020 – 2021 “Pemodelan Teoritis Resonansi Magnetik Inti pada Logam Berat” from Univ. Indonesia
2020 – 2021 “Pemodelan Teoritis Efek Spin Transfer Torque pada Logam Berat” from Univ. Indonesia
2020 – 2021 “Kajian Teoretis Efek Impuritas Permukaan pada Sifat Magnetis Logam Berat” from Univ. Indonesia
2020 – 2021 “Kajian Teoretis Transfer Energi Spin dalam Baterai Berbasis Spin Nuklir” from Univ. Indonesia
2015 – 2018 “Antiferromagnetic spin Seebeck effect” from JSPS
2015 – 2018 Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS) Fellowship for Young Scientists.
2008 – 2015 Japanese Ministry of Education and Sport (MEXT) Scholarship.
Research Interest
Recently published
Hyperfine interactions enable spin-orbit torque on nuclear spin
Hyperfine interactions describe the magnetic interaction between spins of atomic nucleus and electron. The interaction, also referred as hyperfine coupling, consists of Fermi contact and dipolar interactions between dipole magnetic moments of atomic nucleus and electron. We demonstrate that the hyperfine coupling can mediate the application of spin-orbit torques acting on nuclear spins. In quantum computing, nuclear spin is a candidate for qubit. Since qubit has the potential to the miniaturization of memory, the application of nuclear spin by means of nuclear spin orbit torque could lead to further miniaturization of spintronics devices.
Spin-orbit couplings at magnetic interface generate magnetoelectric effect and enable exchange bias
Exchange bias is a unidirectional magnetic anisotropy that often arise from interfacial interaction of a ferromagnetic and antiferromagnetic layers. we show that spin-orbit couplings in magnetic heterostructures, such as La2/3Sr1/3MnO3|LaAlO3|SrTiO3 can induces an exchange bias via an interface magnetoelectric effect. The interface magnetoelectric effect is induced by spin-orbit couplings that arises from the broken symmetry of the system. We demonstrate that the exchange bias can be controlled by electric field.
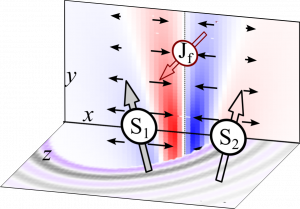
Twisted spin density generates anisotropic magnetic interactions.
The interactions of spins -most miniature magnets- can be isotropic or anisotropic, the latter resulting in twisted spin orientations. This article finds a simple explanation of the anisotropic interaction named Dzyaloshiskii-Moriya in metals. The model is based on two atomic spins; one of them is heavy, such as a lanthanide. As a result, a spin orientation emerges in the electrons of the metal and is perpendicular to the atomic spins. We name this as Dzyaloshisnkii-Moriya Spin-Density (DM-SD). When additional magnetic atoms are considered, the DM-SD mediates their interaction, similar to the magnetic field of large magnets’ poles, or the isotropic polarization in metals connecting far spins. The figure shows three spins (one of them, Jf, a lanthanide) and the DM-SD (colormap and small arrows) mediating their exchange.
Orbital hybridization enhances interface phenomenon
In chemistry, the mixing of atomic orbitals form orbital hybridization. The orbital hybridization helps to explain molecule shape. In a carbon atom, for example, s and p orbitals form s-p orbital hybridization. In the band theory of solid state, orbital hybridization can also occur. For example, in the Anderson impurity model, an impurity in a sea of conduction electrons is modeled as a localized orbital and an itinerant orbital. The orbital hybridization enables the interaction between the bands. In this article, we study a spin current generation phenomenon at the interface of a magnetic material and a heavy metal. The heavy metal can be described using a generalized Anderson model with s-d orbital hybridization. By comparing the data of various heavy metals, we show that the s-d orbital hybridization enhances the spin current generation.
Book:
A.B. Cahaya, Fungsi khusus dan persamaan diferensial dalam fisika matematika (UI Publishing, Jakarta, 2022).
Student Projects
Theoretical Condensed Matter Physics (students of Theoretical/Computational Condensed Matter Physics Research Group, etc):
- 2020-2021:
- Faisal Kengo, Effect of Layered Dielectric Structure Variation on Light Absorption and Electric Field in Atomic Layer Material
- Muhammad Aziz Rahman, Tight-Binding Model for Graphene C-13: Investigating the Role of Electron-Phonon Coupling
- Muhammad Fadli Rais, Calculation of Light Absorption in Semiconductors with Quadratic, Quartic, and Sextic Energy Dispersions
- Rico M. Sitorus, Theoretical Modeling of Magnetic Susceptibility of Pd and Pt
- Rudye Layton, Theoretical Study of Valley Polarization in Anitimonene using Circularly-Polarized Light
- 2021-2022
- Janice A. Tombeg, Theoretical Study of Electron, Spin, and Heat Transports in Magnetic Tunnel Junction
- M. Ja’far Prakoso, Theoretical Study of Valley Polarization in Bismuthene using Circularly-Polarized Light
- Bismo Bandutomo, Magnetization Reversal Mechanism of Co/Pt and CoFeB/Pd thin films based on Fatuzzo-Labrune model
- Ansell Alvarez Anderson, RKKY Interaction in Spin Valve Structure with Semiconductor Spacer
- 2022-2023
- Rani Kumalasari Adita Putri, Theoretical Study of Induced Antisymmetric Exchange Interaction at Paramagnetic – Ferromagnetic Interface
Computational Material Physics (students of Exploration and Innovation of Magnetic and Dielectric Materials Research Group, etc)
- 2020-2021
- Wakid Ali Muntoha, Computational Analysis of Reflection Loss from Scattering Parameter of Electromagnetic Wave Absorbing Materials based on Nicolson-Rose-Wear method
- Rafael Ferdinandus Maniru, Law of Approach to Saturation for Determining Magnetic Intrinsic Behavior of BaFe12-xMnx/2Tix/2O19 and SrFe12-xMnx/2Tix/2O19
- 2022-2023
- Zahirah Lesnia Wibawati Chamsudi, Analysis of Stress Ratio due to Thermal Expansion in Piping System using Carbon Steel, Alloy Steel, and Stainless-Steel Materials
Selected Publications
- A.B. Cahaya, A.O. Leon, and M.H. Fauzi, “Spin-orbit torque on nuclear spins exerted by a spin accumulation via hyperfine interactions”, Nanotechnology 34, 505001 (2023)
- A.B. Cahaya, A.A. Anderson, A. Azhar, and M.A. Majidi,”Electrically controllable exchange bias via interface magnetoelectric effect”, IEEE Trans. Magn. 59 (11) 1300304 (2023)
- M.S. Ukhtary, A.R.T. Nugraha, A.B. Cahaya, A. Rusydi, and M.A. Majidi, “High-performance Kerr quantum battery”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 123, 034001 (2023)
- A.B. Cahaya and A.O. Leon, “Dzyaloshinskii-Moriya spin density by skew scattering”, Phys. Rev. B 106, L100408 (2022)
- A.B. Cahaya, R.M. Sitorus, A. Azhar, A.R.T. Nugraha, and M.A. Majidi, “Enhancement of spin-mixing conductance by s-d orbital hybridization in heavy metals”, Phys. Rev. B 105, 211438 (2022)
- A.B. Cahaya, “Enhancement of thermal spin pumping by orbital angular momentum of rare earth iron garnet”, J. Magn. Magn. 553, 169248 (2022)
- M.S. Muntini, E. Suprayoga, S.A. Wella, I. Fatimah, L. Yuwana, T. Seetawan, A.B. Cahaya, A.R.T. Nugraha and E.H. Hasdeo, “Spin-tunable thermoelectric performance in monolayer chromium pnictides”, Phys. Rev. Mater. 6, 064010 (2022)
- A.B. Cahaya, A. Azhar, D. Djuhana and M.A. Majidi, “Effect of interfacial spin mixing conductance on gyromagnetic ratio of Gd substituted Y3Fe5O12“, Phys. Lett. A 437, 128085 (2022)
- A.B. Cahaya, “Adiabatic limit of RKKY range function in one dimension”, J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 547, 168874 (2022).
- A.B. Cahaya and M.A. Majidi, “Effects of screened Coulomb interaction on spin transfer torque”, Phys. Rev. B 103, 094420 (2021)
- A.B. Cahaya, A.O. Leon, M.R. Aliabad and G.E.W. Bauer, “Equilibrium current vortices in simple metals doped with rare earths”, Phys. Rev. B 103, 064433 (2021)
- A.B. Cahaya, A. Azhar and M.A. Majidi, “Yukawa potential for realistic prediction of Hubbard and Hund interaction parameters for transition metals”, Phys. B Condens. Matter 604, 412696 (2021)
- A.O. Leon, J.D.E. Castro, J.C. Retamal, A.B. Cahaya and D. Altbir, “Manipulation of the RKKY exchange by voltages”, Phys. Rev. B 100, 014403 (2019)
- C.N. Rangkuti, A.B. Cahaya, A. Azhar, M.A. Majidi and A. Rusydi, “Manifestation of charge/orbital order and charge transfer in temperature-dependent optical conductivity of single-layered Pr0.5Ca1.5MnO4”, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 31, 365601 (2019)
- A.O. Leon, A.B. Cahaya and G.E.W. Bauer, “Voltage control of rare-earth magnetic moments at the magnetic-insulatorーmetal interface”, Phys. Rev. Lett. 120, 027201 (2018)
- A.B. Cahaya, A.O. Leon and G.E.W. Bauer, “Crystal field effects on spin pumping”, Phys. Rev. B 96, 144434 (2017)
- A.B. Cahaya, O.A. Tretiakov and G.E.W. Bauer, “Spin Seebeck power conversion”, IEEE Trans. Magn. 51, 0800414 (2015)
- A.B. Cahaya, O.A. Tretiakov and G.E.W. Bauer, “Spin Seebeck power generators”, Appl. Phys. Lett. 104, 042402 (2014)








 English
English